Range of Wavelengths to Which Each Cone Type Responds Best
8B model 55. The peak sensitivity is broadly in the blue green and red parts of the visible spectrum for the S M and L cones.
The modeling determined the weightlevel of input from each cone opsin type.
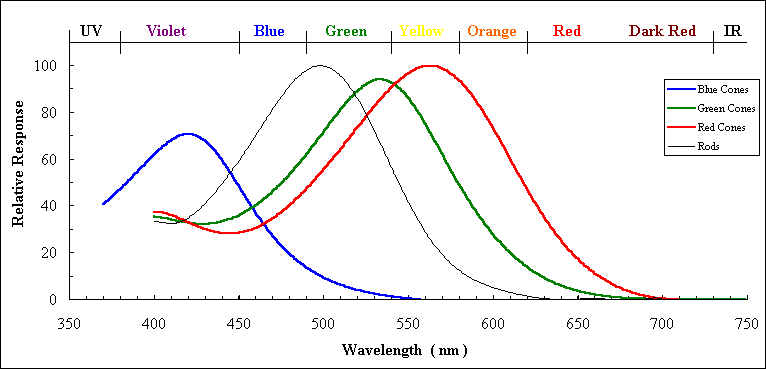
. Identify the range of wavelengths to which each cone type responds best. Despite what often stated the short medium and long cone cells do not represent specific colours. Humans have three types of cones such as long L cone for 560 nm medium M cone for 530 nm and short S cone for 420 nm.
330 nm 370 nm and small yet discernable at longer wavelengths. The Blue Cone is 420nm. Another type responds best to green light and the last type responds best to blueand the last type responds best to blue light.
The response curve of a Short l Cone overlaps little with Medium and Long - See graph of Receptor Response vs. Each one is specialising at detecting a particular range of wavelengths. The ratio of activity across the three types of cones determines the color.
The three types of cones in the human eye each contain a photo-sensitive pigment that has the capacity to absorb a range of light wavelengths. The best-fitting model Fig. One type responds best to red light.
Although each cone class responds best to a small range of wavelengths they all respond in some way. We have 3 types of cones in our eyes as well as rods rods are for brightness so dont really apply here One type of cone is primarily sensitive to red one to green and one to blue. Each cone is characterized by the wavelength at which maximum or peak absorption occurs.
-respond the most to shorter wavelengths a little to medium wavelengths and not at all to longer wavelengths M-cones -respond best to medium wavelength photons perceived as green to. The degree of stimulation of each of the three cone types determines the strength of the neuronal impulses along that. The third type responds the most to short-wavelength light peaking at 420 nm and is designated S for short and these make up only around 2 of the cones in the human retina.
Well thats because we do. The photoreceptors are all sensitive to a broad range of wavelengths albeit different types of photoreceptors have a peak sensitivity at different wavelengths. Could match any color by mixing appropriate amounts of just three wavelengths from PSYC 451 at Maryville University.
The second most common type responds the most to light of medium-wavelength peaking at 530 nm and is abbreviated M for medium making up about a third of cones in the human eye. Each of which responds primarily to a specific range of wavelengths. Asked Feb 7.
More intense light increases the brightness of the color but does not change the ratio. Cone cells or cones are photoreceptor cells in the retinas of vertebrate eyes including the human eyeThey respond differently to light of different wavelengths and are thus responsible for color vision and function best in relatively bright light as opposed to rod cells which work better in dim lightCone cells are densely packed in the fovea centralis a 03 mm. When one of those cone types activate the brain interprets their signal as colour.
Instead light with a wavelength of light to which we assign the color Blue from 450 to 490 nm give or take actually stimulates each of the three cone types with roughly comparable effectiveness. 530nm Long l. A Blue and red b Red and green.
With each wavelength of light each of the receptors reacts to a different degree and certain receptors prefer one wavelength says Brian Timney PhD a researcher of mammalian vision who is dean of social science at the University of Western Ontario. D Each of the three cone types red long green medium and blue short responds to a different range of light wavelengths. There are three basic types of cones in the human retina each of which responds maximally to a different wavelength.
Three kinds of cones are unevenly distributed. To which wavelengths of light do the three cone types of the retina respond maximally. The Red Cone is 560nm.
The light will not be responded to at all because that wavelength is invisible. These work together to help us perceive colors in the world. Given below is a graph showing relative response of rods and cone cells in different wavelengths of light.
Since a visual pigment does not respond to only one wavelength but responds to wavelengths flanking the. Range will stimulate all three cone types to different degrees but mainly stimulate the green cone receptors. Identify the range of wavelengths to which each cone type responds best.
Asked Aug 9 2019 in Psychology by lpngal. The diagram above shows how strongly each cone cell type reacts to different wavelengths. In color vision blue-violet cones are most sensitive to wavelengths red cones to wavelengths and green cones to asked Apr 8 2017 in Psychology by Entafsha general-psychology.
The figure represents the sensitivity of each of those cone-types as functions of the wavelength of light. A cone system that responds to specific wavelength will respond while other cone systems will be silent. Likewise we perceive yellow orange or red depending on the relative activation of green and red cones.
Cones - So they respond to very different ranges of light - ie. Which of the cone cells will respond to wavelengths in the orange region. Each cone responds to a broad range of wavelengths but some more than others.
So do you mean how do we see purple if we dont have a purple cone. Cone cells and rod cells. Each type of cone cell responds to a range of wavelengths with a particular wavelength showing the maximum response.
The Green Cone is 530nm. Our eyes have two types of photoreceptors. B Rod photoreceptors respond best to a greenish - yellow light but also respond weakly to lights that are red or violet.
Cone cells respond to color and there are three types. Where is the blind spot optic disc located ian relation to the fovea. 3 overlapping curves for 3 Cone types - Short l Cones give best response to 420nm Med l.
Where is the blind spot optic disc located ian relation to the fovea. All three cone systems will respond at varying strengths. For one thing those three cone-types are not monochromatic that is they dont only respond to one wavelength but rather each responds to a wide range of wavelengths that overlap.

Cone Cells In Human Eye Are Responsible For Color Vision The Cone Cells Are Of Three Types Red R Green G And Blue B Cells Each Type Of Cone Cell Responds To
Is The Range Of Wavelengths The Light Detectors Rods In Our Eyes Can See The Same As The Range Our Colour Receptors Cones Can See If So Is This A Coincidence

The Cone Spectral Sensitivity Functions At All Wavelengths In The Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Range of Wavelengths to Which Each Cone Type Responds Best"
Post a Comment